조합
서로 다른 n 개 중 r개를 선택하는 경우의 수 (순서 x, 중복 x)
ex) 서로 다른 4명 중 주번 2명 뽑기
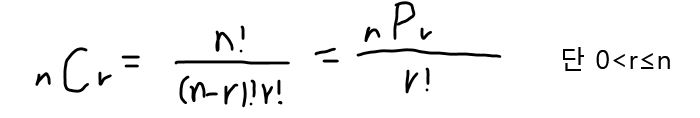
int n = 4;
int r = 2;
int pResult = 1; //순열 구하기
for (int i = n; i >= n- r +1; i--) {
pResult *= i;
}
int rResult = 1; //r!구하기
for (int i = 1; i <= r ; i++) {
rResult *= i;
}
System.out.println("결과: " + pResult/ rResult); // 순열/r!중복 조합
서로 다른 n개 중 r개를 선택하는 경우의 수.
단, 이 때에는 (순서 x, 중복 o)
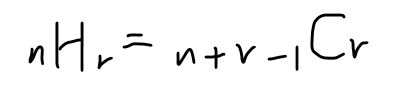
static int getCombination(int n, int r) {
int pResult = 1; //순열 구하기
for (int i = n; i >= n- r +1; i--) {
pResult *= i;
}
int rResult = 1; //r! 구하기
for (int i = 1; i <= r ; i++) {
rResult *= i;
}
return pResult/rResult; //순열/r!
}
//중복조합 구하기
n = 2;
r = 3;
System.out.println("결과: " + getCombination(n+r-1, r));
ex) 후보 2, 유권자 3명일 때의 무기명 투표

1,2,3,4 이용 => 세자리 자연수 만들기
public class Practice {
void combination(int[] arr, boolean[] visited, int depth, int n, int r) {
if(r == 0){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(visited[i]) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
if(depth == n) {
return;
}
visited[depth] = true;
combination(arr,visited, depth+1, n, r-1);
visited[depth] = false;
combination(arr,visited,depth+1,n,r);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
boolean[] visited = {false, false, false, false};
Practice p = new Practice();
p.combination(arr, visited, 0, 4, 3);
}
}
하나하나 살펴보자.
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4}; //배열생성
boolean[] visited = {false, false, false, false}; //visited배열 생성
Practice p = new Practice(); //객체 생성
p.combination(arr, visited, 0, 4, 3); //메서드 combination 호출
//depth = 0, n = 4, r = 3
visited[depth] = true;
combination(arr,visited, depth+1, n, r-1);방문했다는 흔적을 위해 visited를 true로 바꿔줌. visited[0] = 1이 된다. combination(arr, visited, 1,4,2)를 호출한다.
(depth : 1, r : 2)
visited[depth] = true;
combination(arr,visited, depth+1, n, r-1);if 문에서 해당사항이 없으므로 쭉 내려와서 visited[depth] 는 2, r은 1이 되어 한번 더 호출된다.
visited[3]은 1 , depqth : 3, r : 0이 된다.
r이 0이 됐으므로 if 문이 시행된다.
if(r == 0){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(visited[i]) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
if(depth == n) {
return;
}if문에서 n이 4이므로 i는 3까지 진행되고 visited[i]가 true일 때 arr[i]가 출력된다. 따라서 123이 출력되고 다시 return한다.
결과 : 123
visited[depth] = true;
combination(arr,visited, depth+1, n, r-1); // 여기로 return
visited[depth] = false; //진행
combination(arr,visited,depth+1,n,r);다음이 진행되어 vistied[3] = 0(현재 1,1,0,0)이 되고 combination(arr,visited,2+1,4,1)을 호출한다.
반복하여 다시 visited : {1,1,0,1} 이 된다. 그리고 combination(arr,visited, 3+1, 4, 1-1)을 호출한다.
if(r == 0){ //여기에 걸림.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(visited[i]) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
if(depth == n) {
return;
}다시 r 이 0이므로 if문에 걸려 visited가 true인 것을 출력하고 return한다. 결과 : 124
visited[depth] = true;
combination(arr,visited, depth+1, n, r-1); //여기로 return
visited[depth] = false;
combination(arr,visited,depth+1,n,r);아래를 진행하여 visited : {1,1,0,0}이 된다. 그리고 combination을 호출한다. 이때 depth는 3, r은 1
따라서, combination(arr,visited, 4,4,1)로 호출된다.
if(r == 0){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(visited[i]) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
if(depth == n) { //여기에 걸림.
return;
}depth 랑 n이 같으므로 다시 return 된다.
visited[depth] = true;
combination(arr,visited, depth+1, n, r-1);
visited[depth] = false;
combination(arr,visited,depth+1,n,r); //여기로 리턴!이대로 한번 끝나고 다시 depth 가 1일때로 돌아가서 visited[depth] = false;부터 다시 반복한다.
결과
1 2 3
1 2 4
1 3 4
2 3 4'기초수학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 제곱과 로그 (0) | 2024.02.27 |
|---|---|
| 점화식(Recurrence), 재귀함수 (0) | 2024.02.27 |
| 순열(Permutation), 팩토리얼(Factorial) (0) | 2024.02.27 |
| 경우의 수 (합의 법칙, 곱의 법칙) (0) | 2024.02.26 |
| 집합(Set)이란? (0) | 2024.02.26 |